Medical Uses of Cannabis for Gastrointestinal Issues: A Guide to Beneficial Compounds
Introduction
Cannabis, commonly known as marijuana, is a complex plant containing a myriad of chemical compounds, including cannabinoids. These compounds interact with the human endocannabinoid system, which plays an essential role in regulating physiological balance. This article delves into the key compounds in cannabis that show promise for the treatment of gastrointestinal (GI) disorders, underpinned by scientific research.
Cannabidiol (CBD): An Anti-Inflammatory Powerhouse
Overview
Cannabidiol (CBD) is one of the most well-studied non-intoxicating cannabinoids in cannabis. CBD has exhibited a broad spectrum of therapeutic potential, including anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antiemetic effects.
GI Applications
Research indicates that CBD’s anti-inflammatory properties can mitigate gut inflammation, a prevalent factor in GI conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and Crohn’s disease. CBD also shows promise in regulating gastrointestinal motility, which could alleviate symptoms like diarrhea and excessive bowel movements.
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC): Beyond Psychoactivity
Overview
Though mainly recognized for its psychoactive properties, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) has medicinal applications relevant to GI health. THC interacts with cannabinoid receptors in the digestive system to influence gut motility, pain perception, and appetite.
GI Applications
For patients suffering from GI disorders like IBD and IBS, THC can relieve cramping and abdominal pain. Additionally, THC possesses antiemetic properties, helping to reduce nausea and vomiting—common symptoms across various GI issues.
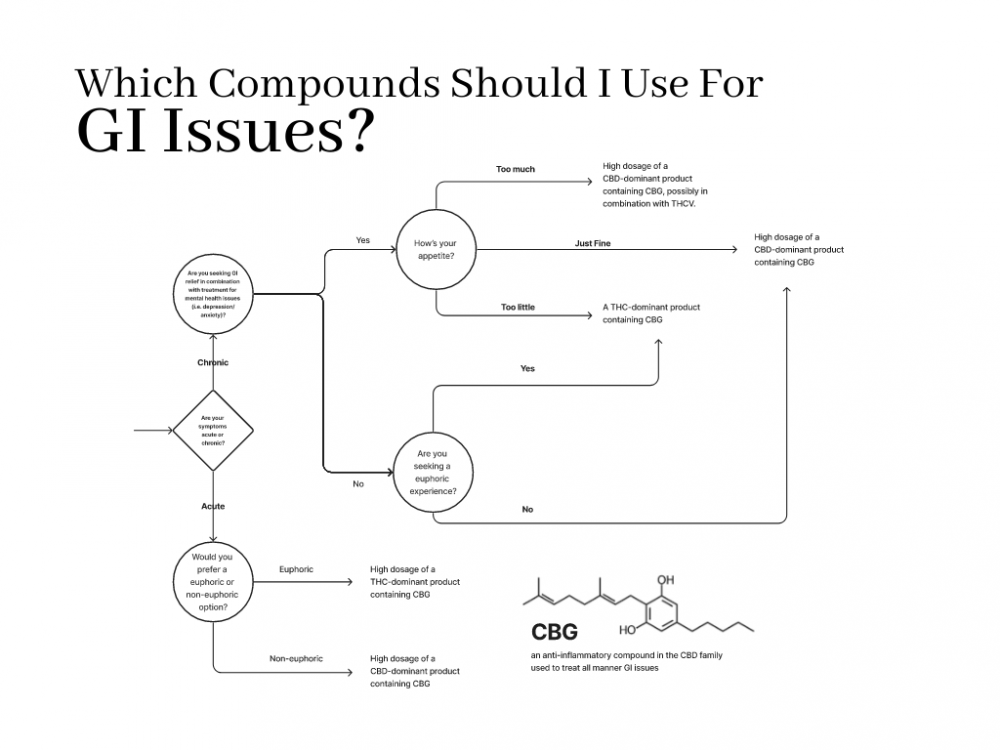
Cannabigerol (CBG): The Understudied Marvel
Overview
Cannabigerol (CBG) is another intriguing cannabinoid present in cannabis, albeit in smaller concentrations compared to CBD and THC. Despite its scarcity, CBG has exhibited remarkable therapeutic potential.
GI Applications
CBG’s anti-inflammatory properties indicate its potential for treating GI conditions associated with inflammation of the gut. It may also alleviate oxidative stress, a contributing factor to the onset and progression of GI disorders.
Beta-Caryophyllene (BCP): More Than Just Aroma
Overview
Beta-caryophyllene (BCP) is a terpene that contributes to the aroma and flavor of cannabis. Beyond its olfactory role, BCP exerts medicinal effects by acting on cannabinoid receptors, particularly those connected to inflammation.
GI Applications
Studies show that BCP has significant anti-inflammatory capabilities, offering therapeutic potential for conditions like colitis. This suggests that BCP could support the management of GI disorders by inhibiting inflammatory responses within the digestive system.
Cannabis is replete with compounds that offer therapeutic benefits for gastrointestinal issues. CBD has proven anti-inflammatory and antiemetic properties, THC can relieve pain and nausea, CBG offers anti-inflammatory and antioxidant benefits, and BCP has anti-inflammatory potential. Ongoing research is crucial for a fuller understanding of how these compounds work, but current findings suggest that cannabis-based treatments offer promising options for GI health. Before adopting any cannabis-related treatments, it is vital to consult healthcare professionals familiar with medical cannabis.
Note: Always consult with healthcare providers knowledgeable about medical cannabis before integrating it into any treatment plan.
📗 Note: Sure, this diagram was fun, but who stops at just one hit? Toke up the full range of knowledge with “The Doctor-Approved Cannabis Handbook” here 📗.

Summary Notes
Harnessing Cannabis for Gastrointestinal Health: A Comprehensive Guide
The exploration of cannabis for treating gastrointestinal (GI) issues illuminates its potential in addressing a broad spectrum of conditions, from inflammatory bowel diseases like Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis to irritable bowel syndrome and motility disorders. Cannabinoids, particularly THC and CBD, have demonstrated efficacy in symptom management, offering relief from pain, inflammation, and nausea, among other symptoms.
Understanding the endocannabinoid system’s role in gastrointestinal health is key to unlocking cannabis’s therapeutic potential. The presence of cannabinoid receptors throughout the GI tract suggests a direct mechanism through which cannabis can exert its effects, impacting processes such as motility, pain sensation, and immune response.
Clinical trials and patient-reported outcomes highlight the benefits and challenges of incorporating cannabis into treatment regimens for GI disorders. Safety concerns and dosage guidelines remain paramount, emphasizing the need for personalized therapy approaches and careful monitoring.
The legal and regulatory landscape surrounding medical cannabis use for gastrointestinal conditions varies by jurisdiction, affecting patient access and research opportunities. As the field advances, educating healthcare providers and patients on the effective, safe use of cannabis becomes increasingly important.
Future research directions promise to deepen our understanding of how specific cannabis compounds and strains can be optimized for gastrointestinal therapy. The integration of cannabinoids into holistic treatment plans underscores the potential for cannabis to enhance quality of life for individuals with GI disorders, paving the way for innovative therapeutic strategies in digestive health.

