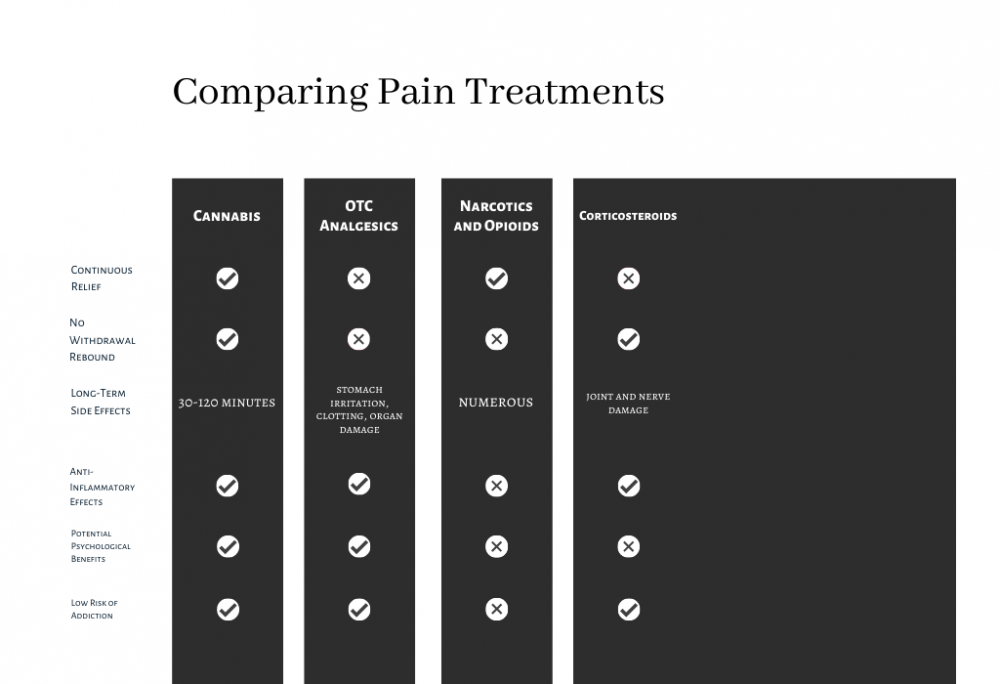
A Comparative Analysis of Pain Treatments: Cannabis Versus Conventional Methods
Pain is a multi-faceted experience with significant implications for our overall quality of life. In the expanding world of medicine, cannabis has emerged as a potential alternative for pain management. This article aims to contrast cannabis-based treatments with traditional, non-cannabis alternatives, underlining the scientific rationale for their effectiveness.
Introduction to Cannabinoids and the Endocannabinoid System
Cannabis comprises over 100 compounds known as cannabinoids, with tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) being the most prominent. THC is mainly accountable for cannabis’ psychoactive effects, while CBD offers a range of therapeutic benefits without intoxication.
Cannabinoids interact with our endocannabinoid system (ECS), a complex cellular signaling network consisting of receptors, enzymes, and endogenous cannabinoids. The ECS serves to maintain internal equilibrium, affecting an array of physiological functions, including pain perception.
Mechanisms of Cannabis-Based Pain Management
THC: The Analgesic Agent
One of the key features of cannabis in pain treatment is its ability to act as an analgesic or a pain reliever. THC interacts directly with cannabinoid receptors in the brain and spinal cord, thereby diminishing the perception of pain.
CBD: The Modulator
CBD enhances the functioning of endogenous cannabinoids, leading to reduced pain and inflammation without producing psychoactive effects.
The Anti-Inflammatory Benefits
Cannabinoids possess additional anti-inflammatory properties, which reduce the secretion of inflammatory molecules. This can be especially beneficial for conditions like arthritis, where inflammation is a primary contributor to pain.
Limitations and Considerations for Cannabis-Based Treatments
While promising, cannabis isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. Its effectiveness can differ based on individual factors, dosage, and the type of pain involved. Clinical trials have investigated its application in various kinds of pain, including chronic, neuropathic, and cancer-related, producing mixed results. Further research is necessary to establish its efficacy conclusively.
Conventional Pain Management Options
Over-the-Counter Medications
Traditional options like ibuprofen or acetaminophen target pain receptors or diminish inflammation, similar to their cannabis-based counterparts.
Prescription Opioids
Despite their effectiveness, opioids pose significant risks due to their addictive nature and potential for overdose, highlighting the need for alternative treatments.
Making an Informed Decision
Selecting the best course of action necessitates an examination of the patient’s unique condition, medical history, and the potential side effects tied to each treatment option. It’s highly recommended to consult healthcare professionals specialized in pain management to devise a tailored treatment plan.
Conclusion
Cannabis-based treatments offer promising avenues as either complementary or alternative options in pain management. The cannabinoids in cannabis, notably THC and CBD, leverage the endocannabinoid system to potentially alleviate pain and inflammation. Nevertheless, the effectiveness of cannabis treatments can be variable, underscoring the need for further research and personalized medical consultation for optimal pain management.
📗 Note: This diagram’s a cameo. Ready for the starring role? Get “The Doctor-Approved Cannabis Handbook” here 📗
If you want personalized guidance or care, consider reaching out to Dr Caplan at CED Clinic

Summary Notes
A Comparative Analysis of Pain Treatments: Cannabis Versus Conventional Methods
The management of pain, a critical and complex aspect of healthcare, has increasingly considered cannabis as a viable treatment alongside, or as an alternative to, conventional methods. This comparative analysis aims to shed light on the effectiveness, safety, and patient experiences associated with using cannabis for pain relief compared to traditional pain treatments, such as opioids and NSAIDs.
Cannabis’s role in pain management, particularly for chronic pain, has been bolstered by evidence suggesting its potential to alleviate discomfort without the high risk of addiction associated with opioids. However, understanding the nuanced efficacy of components like CBD and THC is crucial in determining their place in pain therapy. CBD oil, for instance, has garnered attention for its anti-inflammatory properties and minimal side effects, presenting a stark contrast to the gastrointestinal risks linked to long-term NSAID use.
The safety profile of cannabis, when weighed against opioids, reveals a significantly lower risk of overdose and dependency, although the long-term effects of cannabis use require further research. Patient testimonies and clinical trials provide valuable insights into the quality of life improvements reported by those who have integrated cannabis into their pain management regimen, highlighting reduced pain levels and enhanced overall well-being.
Legal considerations remain a formidable barrier to access for many, with cannabis’s status fluctuating widely between jurisdictions. This legal variability impacts not only patient access but also the scope of research and clinical trials necessary to fully understand cannabis’s potential in pain management.
Cost analysis also plays a pivotal role in the discussion, as the economic burden of chronic pain treatments is substantial for both individuals and healthcare systems. Cannabis, with its varied administration methods—including topicals, edibles, and inhalables—offers a range of options that may prove more cost-effective in some contexts compared to expensive prescription medications.
Transitioning from conventional pain medications to cannabis involves careful consideration of factors such as dosing, potential drug interactions, and patient preferences. Guidelines for this transition, as well as for the integration of cannabis into multidisciplinary treatment plans, are evolving, reflecting the need for personalized and informed approaches to pain management.
As research continues to advance, the comparative analysis of cannabis versus conventional pain treatments will undoubtedly become more nuanced, informed by patient outcomes, pharmacological studies, and the development of innovative cannabis-based therapies. The future of pain treatment may well embrace cannabis as a central component, offering hope for effective, safe, and patient-centered approaches to pain relief.


