The Rise of Medical Cannabis in Pain Management
Medical cannabis, also known as medical marijuana, is increasingly being recognized for its potential role in pain treatment. This article delves into the underlying mechanisms of cannabis, its primary compounds, and the existing scientific literature that supports its medical applications.
Key Compounds: THC and CBD
Cannabis boasts over 100 chemical compounds known as cannabinoids. Of these, THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol) are the most significant. THC is the compound responsible for the psychoactive effects or the “high” associated with cannabis. Conversely, CBD does not induce a high and is gaining attention for its prospective therapeutic advantages.
The Endocannabinoid System: How Cannabis Interacts with the Body
When ingested or inhaled, cannabinoids like THC and CBD engage with the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS). The ECS is vital for maintaining homeostasis within the body and comprises cannabinoid receptors found predominantly in the brain, immune system, and peripheral tissues.
THC and the ECS
THC mainly targets CB1 receptors in the brain, resulting in psychoactive effects and pain relief. It can disrupt pain signal transmission, consequently altering pain perception.
CBD and the ECS
Unlike THC, CBD does not directly bind to CB1 receptors but can modulate them indirectly. This modulation influences various physiological processes, potentially leading to anti-inflammatory, analgesic (pain-relieving), and anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing) outcomes.
Research Findings: Efficacy in Pain Management
The potential medical utilities of cannabis are expansive, with pain management standing out as a key area. Studies suggest that cannabis could be effective for chronic pain, neuropathic pain, and pain related to conditions like multiple sclerosis and cancer.
For instance, research published in the Journal of Pain indicated that inhaled cannabis significantly diminished pain intensity and enhanced sleep quality in patients with chronic neuropathic pain. Another study in the Annals of Internal Medicine reported that cannabis extracts or synthetic cannabinoids could effectively treat chronic pain.
Additional Therapeutic Benefits: Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Cannabis may also have anti-inflammatory attributes that could benefit people with conditions like arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and inflammatory bowel disease. CBD, in particular, has demonstrated potential in mitigating inflammation and immune system responses.
Caveats and Considerations
It’s crucial to note that medical cannabis is not a panacea; its effectiveness can vary from person to person. Its usage should be overseen by healthcare professionals, especially considering potential side effects, drug interactions, and varying legal frameworks.
Conclusion: A Promising but Complex Solution for Pain Relief
Medical cannabis, with its key compounds THC and CBD, interacts with our body’s endocannabinoid system to offer potential pain relief and other therapeutic benefits. Although scientific research points to its efficacy in pain management and inflammation reduction, individual responses can differ. As such, comprehensive medical supervision remains crucial.
📗 Note: If this diagram is just the bud, wait till you read “The Doctor-Approved Cannabis Handbook.” Cultivate your knowledge by clicking this link 📗.

Summary Notes
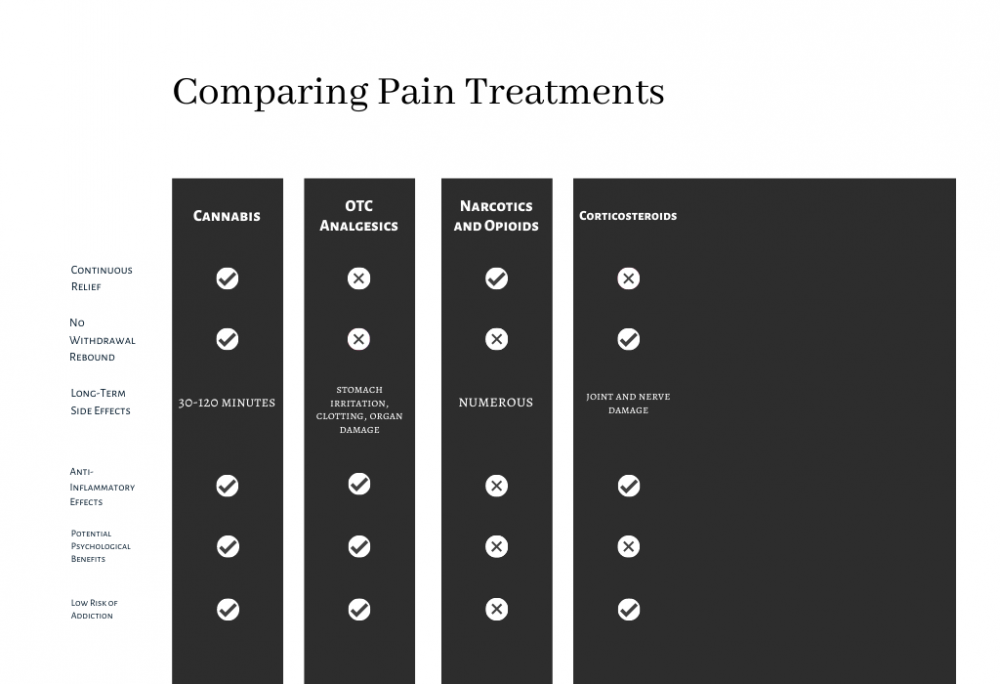
Exploring Pain Treatment Options: Narcotics, Opiates, and Over-the-Counter Alternatives
The comparison of pain treatments, including narcotics, opiates, and over-the-counter (OTC) options, is essential for understanding the broad spectrum of strategies available for pain management. Evaluating the efficacy, safety, and mechanisms behind these treatments helps healthcare providers and patients make informed decisions tailored to individual needs and conditions.
Narcotics and opiates offer potent pain relief but come with significant risks such as dependency and withdrawal, prompting a closer look at non-addictive alternatives and OTC options like NSAIDs. Innovations in pain management are continually emerging, offering new hope for effective relief without the adverse effects associated with traditional narcotic use.
As research advances, a comprehensive approach that includes understanding patient experiences, gender and age differences, and the pharmacokinetics of various pain treatments becomes crucial. This holistic view aids in developing personalized, safe, and effective pain management plans that consider the complexities of pain and its impact on individuals’ lives.
The future of pain treatment lies in the balance between utilizing advanced research to improve existing therapies and exploring new, innovative options that prioritize patient safety, efficacy, and quality of life.


