Preseizure Symptoms and Types of Seizures
Preseizure Symptoms
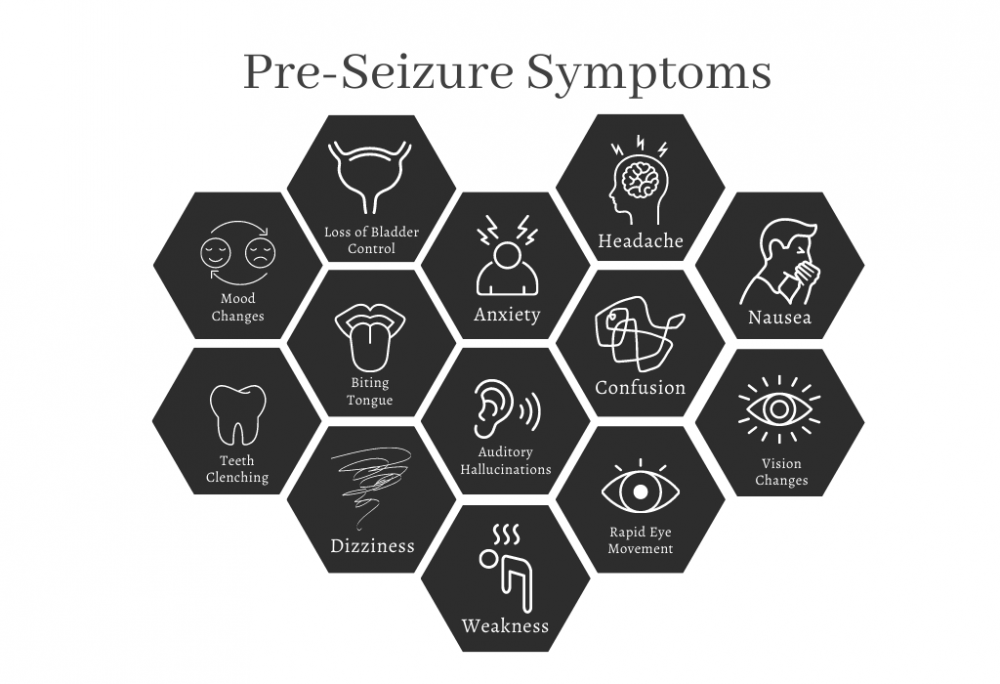
Preseizure symptoms, also known as “aura,” vary greatly among individuals. These symptoms can include:
- Mood Changes: Significant changes in mood, often described as a feeling of impending doom (Mula et al., 2008).
- Loss of Bladder Control: Urinary incontinence before or during a seizure (Tellez-Zenteno et al., 2004).
- Anxiety: Heightened emotional state (Mula et al., 2008).
- Pain: Rare but possible, especially abdominal pain (Stewart et al., 2001).
- Headache: A sense of pressure or tightness in the head (Friedman et al., 2018).
- Nausea: Feeling of sickness or urge to vomit (Stewart et al., 2001).
- Vision Changes: Flashes of light or blind spots (Hennessy et al., 2001).
- Confusion: Mental disorientation (Benbadis et al., 2000).
- Rapid Eye Movements: Uncontrolled eye movements (Benbadis et al., 2000).
- Weakness: Sudden loss of muscle strength (Mula et al., 2008).
- Auditory Hallucinations: Hearing sounds that are not present (Benbadis et al., 2000).
- Biting Tongue: Involuntary tongue biting (Friedman et al., 2018).
- Dizziness: Feeling lightheaded or vertiginous (Hennessy et al., 2001).
- Teeth Clenching: Involuntary jaw tightening (Friedman et al., 2018).
Types of Seizures
- Absence Seizures: Brief episodes of staring or inattention.
- Tonic Seizures: Sudden muscle stiffness.
- Clonic Seizures: Rhythmic muscle jerking.
- Mixed Seizures: Combinations of the above symptoms.
Comparison Table: Medication Types
| Types of Seizures | Conventional Medications | Cannabinoids | Used for Prevention/Rescue |
|---|---|---|---|
| Absence | Ethosuximide, Valproate | CBD | Prevention |
| Tonic | Benzodiazepines, Phenytoin | CBD, THC | Both |
| Clonic | Benzodiazepines, Valproate | CBD | Both |
| Mixed | Lamotrigine, Topiramate | CBD, THC | Prevention |
Precautions with Cannabinoids
Individuals with liver conditions, cardiovascular issues, or other medical illnesses should exercise caution with cannabinoid use and consult Dr. Caplan at CED Clinic for a personalized treatment plan.
References
- Mula, M., et al. (2008). Peri-ictal psychopathology: An overview. Journal of Neuropsychiatry, 20(4), 427-433.
- Tellez-Zenteno, J. F., et al. (2004). Long-term seizure prognosis in epilepsy patients treated with and without surgery. Neurology, 63(12), 2312-2313.
- Stewart, M., et al. (2001). Symptoms of depression and anxiety in pediatric epilepsy patients. Epilepsia, 42(6), 789-794.
- Friedman, D., et al. (2018). Somatic sensations of aura. Neurology, 91(17), 787-793.
- Hennessy, M. J., et al. (2001). Symptoms of depersonalization and autoscopic phenomena. Neurology, 57(5), 839-841.
- Benbadis, S. R., et al. (2000). The differential diagnosis of epilepsy: A critical review. Epilepsy & Behavior, 1(4), 276-284.
- O’Connell, B. K., Gloss, D., & Devinsky, O. (2017). Cannabinoids in treatment-resistant epilepsy: A review. Epilepsy & Behavior, 70, 341-348.
- Devinsky, O., et al. (2017). Cannabidiol in patients with treatment-resistant epilepsy: an open-label interventional trial. The Lancet Neurology, 15(3), 270-278.
Note: Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for a personalized treatment plan.
📗 Note: You’ve just had a sip; now it’s time for the whole cup. Quench your thirst for wisdom with “The Doctor-Approved Cannabis Handbook” here 📗

Summary and Search Terms
Preseizure Symptoms and Types of Seizures: A Detailed Examination
Understanding preseizure symptoms and the various types of seizures is crucial for individuals with epilepsy or those caring for someone with seizure disorders. Recognizing these signs can significantly aid in managing the condition effectively and ensuring safety during a seizure event.
Identifying preseizure symptoms, such as aura sensations or sudden changes in mood or sensation, can provide crucial warning of an impending seizure, allowing for preparation and the implementation of safety measures. The early signs of an impending seizure might vary widely among individuals, making personal observation and documentation essential for effective management.
Seizures are classified into several types, each with distinct characteristics. Generalized seizures affect both sides of the brain simultaneously and include tonic-clonic, absence, and myoclonic seizures, among others. Focal seizures, previously known as partial seizures, originate in a specific area of the brain and can be simple (without loss of consciousness) or complex (with impairment of consciousness).
Understanding the differences between generalized and focal seizures is vital for diagnosis and treatment. For instance, temporal lobe seizures, a type of focal seizure, may involve unusual sensations like deja vu, fear, or auditory hallucinations. In contrast, absence seizures, typically occurring in children, manifest as brief lapses in awareness that might be mistaken for daydreaming.
Recognizing the signs of more severe seizure types, such as tonic-clonic seizures, which involve loss of consciousness and violent muscle contractions, is imperative for providing immediate and appropriate care. Similarly, awareness of non-epileptic seizures, which may have psychological rather than neurological origins, is important for ensuring accurate diagnosis and treatment.
The postictal state, a period following the cessation of seizure activity, can involve confusion, fatigue, and other symptoms, further emphasizing the need for comprehensive care and observation post-seizure.
Diagnosing seizure disorders involves a thorough assessment, including neurological evaluations and possibly imaging studies, to determine the seizure type and underlying causes. This diagnostic process guides the selection of appropriate treatment options, which may include medication, lifestyle adjustments, or, in some cases, surgical interventions.
As research and understanding of epilepsy and seizure disorders continue to evolve, so too do the strategies for managing preseizure symptoms and different types of seizures. By staying informed and vigilant, individuals affected by seizures can achieve better outcomes and improved quality of life.
This detailed examination of pre-seizure symptoms and seizure types highlights the importance of awareness and education in managing epilepsy and seizure disorders. Through early recognition and appropriate response, the impact of seizures on daily life can be significantly mitigated, fostering a safer and more manageable living environment for those affected.

