The Biochemical Pathways of THC and CBD
Understanding the intricate biochemistry of THC and CBD is critical for appreciating how these compounds interact within the human body. From metabolism in the liver to actions on the endocannabinoid system (ECS), these cannabinoids also interact with hormones and neurotransmitters, such as estrogen and dopamine. This involves complex pathways and receptor interactions that can offer therapeutic benefits while also having the potential for adverse effects.
Extensive Comparison Table: THC, CBD, and Biochemical Pathways
| Hormone/Receptor Type | Location in Body | Cannabinoids Involved | Synergistic/Inhibitory | Effect at Doses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CB1 | CNS, Liver | THC | Synergistic | High Doses |
| CB2 | Immune System | CBD | Synergistic | Moderate Doses |
| Estrogen Receptors | Reproductive Organs | THC, CBD | Inhibitory | Moderate Doses |
| Testosterone Receptors | Testes, Muscle | THC | Inhibitory | High Doses |
| Dopamine Receptors | CNS | THC | Synergistic | Moderate Doses |
| Serotonin Receptors | CNS, GI Tract | CBD | Synergistic | Moderate Doses |
| Adrenaline Receptors | CNS, Cardiovascular System | THC | Inhibitory | High Doses |
| Acetylcholine Receptors | CNS, PNS | CBD | Inhibitory | Moderate Doses |
| Noradrenaline Receptors | CNS | THC, CBD | Synergistic | Low Doses |
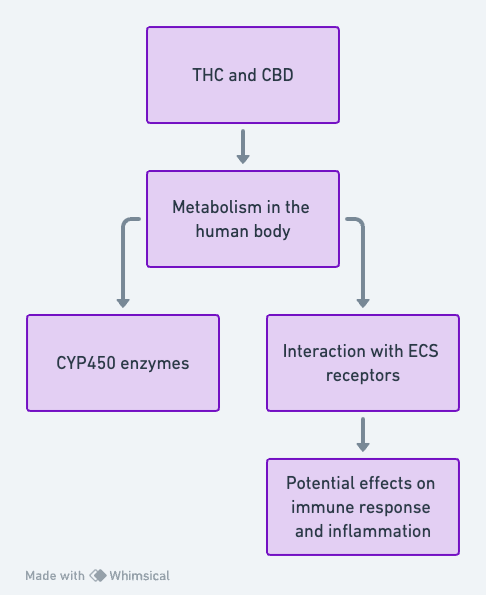
THC and CBD Metabolism
- THC is primarily metabolized in the liver by CYP2C9, CYP2C19, and CYP3A4 enzymes into 11-OH-THC, which is also psychoactive[1].
- CBD is metabolized by CYP3A4 and CYP2C19 into its various metabolites, such as 7-OH-CBD[2].
ECS Receptor Interactions
- THC primarily binds to CB1 receptors, influencing neurotransmission[3].
- CBD has a low affinity for CB1 and CB2 receptors but modulates them indirectly[4].
Hormonal Interactions
- THC decreases testosterone levels through inhibition[5].
- CBD has been shown to interact with estrogen receptors, but the full implications are not yet understood[6].
Neurotransmitter Interactions
- THC increases dopamine release, creating euphoric feelings[7].
- CBD is known to modulate serotonin levels, affecting mood and anxiety[8].
- Both THC and CBD have complex interactions with adrenaline, acetylcholine, and noradrenaline[9].
References:
- Huestis, M. A. Chem Biodivers. 2007.
- Jiang, R., et al. Drug Metab Dispos. 2011.
- Pertwee, R. G. Pharmacol Rev. 2006.
- McPartland, J. M., et al. J Cannabis Ther. 2002.
- Kolodny, R. C., et al. Am J Psychiatry. 1974.
- Eagon, P. K., et al. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2002.
- Tanda, G., et al. Nat Neurosci. 1997.
- Linge, R., et al. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016.
- Gururajan, A., et al. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2010.
Special Notes:
Patients with conditions such as schizophrenia, cardiovascular disorders, or hormone-sensitive cancers should exercise caution with cannabinoids. For personalized, expert consultation, please contact Dr. Caplan at CED Clinic.
📗 Note: The diagram’s your first date; the book is the honeymoon. Fall in love with knowledge here 📗.

In the concluding section of our exploration into “The Biochemical Pathways of THC and CBD,” let’s synthesize the pivotal insights and consider the path forward in cannabinoid research.
Diving deep into THC biochemical effects in the human body and CBD metabolic pathways, we uncover how these cannabinoids distinctly interact with the brain’s receptors and the endocannabinoid system. The differences between THC and CBD biochemical processes are fundamental in understanding their diverse therapeutic potentials, from THC’s mechanisms in pain relief to CBD’s role in reducing anxiety.
The contrasting impact on the central nervous system between THC and CBD highlights the unique science behind THC’s psychoactive effects and CBD’s anti-inflammatory pathways. With detailed studies on molecular interactions and neurotransmitter systems, the comprehensive analysis extends to THC and CBD’s influence on mood, memory, and neuroprotection.
Pharmacokinetics of CBD and THC’s interaction with cannabinoid receptors point towards their significant roles in modulating sleep cycles, pain perception, and appetite. Moreover, their effects on the immune system and stress response mechanisms further illustrate the intricate biochemical pathways these cannabinoids navigate.
Research into THC’s addiction potential and CBD’s modulation pf the body’s homeostasis reveals the dual nature of these compounds, necessitating a nuanced understanding of their benefits and risks. CBD’s influence on stress response mechanisms and its role as a neuroprotective agent showcase its potential in treating a variety of conditions without the psychoactive effects associated with THC.
The exploration of biochemical pathways involved in THC’s addiction potential highlights the importance of cautious use, especially in individuals with a predisposition to substance use disorders. Meanwhile, CBD’s capacity as a modulator of the body’s homeostasis underscores its therapeutic versatility, impacting everything from pain management to mental health.
Scientific insights into THC and CBD’s interaction with other drugs are crucial for developing safe treatment protocols, particularly given the increasing use of cannabinoid-based therapies in conjunction with traditional medications. This area of study promises to elucidate the complexities of cannabinoid pharmacology and its implications for drug interactions and side effects.
As we look toward future research directions in THC and CBD biochemical studies, the potential for groundbreaking discoveries remains vast. Understanding the molecular underpinnings of these cannabinoids will not only advance our knowledge of their therapeutic effects but also pave the way for the development of more targeted and effective treatments. The journey through the biochemical pathways of THC and CBD has only just begun, promising a future where the full spectrum of their benefits can be harnessed in a safe, controlled, and scientifically informed manner.
This deep dive into the biochemical pathways of THC and CBD illuminates the complex interplay between these cannabinoids and the human body. As research continues to unfold, the promise of cannabinoid-based therapies in enhancing health and well-being is more apparent than ever. The exploration of these pathways not only enriches our understanding of cannabis’s pharmacological effects but also holds the key to unlocking new therapeutic potentials for a wide range of conditions.

