Cannabinoid Receptors and Chronic Genetic Diseases
Understanding the role of cannabinoid receptors across various organs is essential, especially in the context of chronic genetic diseases. These receptors are not just confined to the brain but are also found in several other organs, playing diverse roles from modulating pain to affecting metabolic and immune functions. In addition, it’s crucial to understand that cannabinoid action isn’t limited to direct receptor binding. Various enzymes and proteins modulate the endocannabinoid system indirectly, offering additional layers of control and potential therapeutic targets.
Comprehensive Comparison Table of Cannabinoid Receptors
| Receptor Type | Organs Present | Relative Density | Direct/Indirect Binding | Inhibit/Induce | Relevant Cannabinoids |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
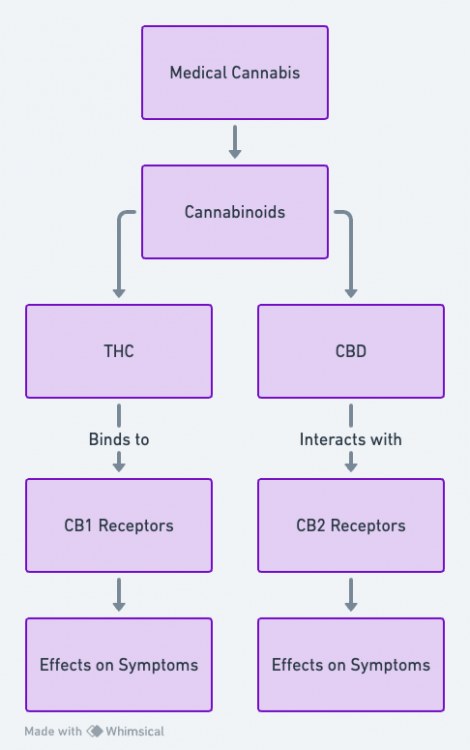
| CB1 | Brain, Liver, Lungs | High in Brain | Direct | Both | THC, Anandamide |
| CB2 | Immune Cells, Spleen, GI tract | High in Immune Cells | Direct | Both | CBD, 2-AG, CBG |
| GPR55 | Brain, Spleen, GI tract | Moderate | Direct | Induce | LPI, CBD |
| TRPV1 | Peripheral Nerves, Brain | Moderate | Direct | Induce | Anandamide, Capsaicin |
| TRPV2 | Immune Cells, Peripheral Nerves | Moderate | Direct | Induce | CBD |
| PPARs | Liver, Kidneys, Heart | Moderate | Direct | Both | Fatty acids, THC |
| 5-HT | Brain, GI tract, Blood Vessels | Moderate | Indirect | Induce | CBD |
| α2-Adrenergic | Brain, Blood Vessels | Low | Indirect | Inhibit | Clonidine, CBD |
| Glycine | CNS, Spinal Cord | Low | Direct | Induce | Glycine, CBD |
| Mu Opioid | CNS, GI tract | Moderate | Indirect | Induce | Endorphins, Enkephalins |
| Delta Opioid | CNS, Peripheral nerves | Low | Indirect | Induce | Endorphins, Enkephalins |
Indirect Cannabinoid Modulators
| Modulator Type | Organs Present | Direct/Indirect | Inhibit/Induce | Relevant Cannabinoids |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FAAH | Brain, Liver | Indirect | Inhibit | Anandamide, PEA |
| MAGL | Brain, Liver | Indirect | Inhibit | 2-AG |
| COX-2 | Most tissues | Indirect | Inhibit | CBD, THC |
| NADA | Brain, Nerves | Indirect | Induce | NADA, Anandamide |
| NMDA | CNS | Indirect | Modulate | Glutamate, NMDA |
| Dopamine | CNS | Indirect | Modulate | Dopamine, CBD |
| GABA | CNS | Indirect | Modulate | GABA, Anandamide |
| Nicotinic ACh | CNS | Indirect | Modulate | ACh, CBD |
| AMT | CNS | Indirect | Inhibit | Anandamide |
| LOX | Most tissues | Indirect | Induce | LA, AA |
References:
- Herkenham, M., et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1991.
- Russo, E. B. Br J Pharmacol, 2011.
- Pertwee, R. G. Curr Med Chem, 2010.
- Matsuda, L. A., et al. Nature, 1990.
- Di Marzo, V., et al. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2015.
- Ahn, K., et al. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2008.
- De Petrocellis, L., et al. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2011.
- Cravatt, B. F., et al. Nature, 1996.
- Mechoulam, R., & Parker, L. A. Annu Rev Psychol, 2013.
Special Notes:
Patients with conditions such as schizophrenia, liver diseases, and cardiovascular disorders should exercise caution. For personalized, expert consultation, reach out to Dr. Caplan at CED Clinic.
📗 Note: If the diagram’s a nibble, the book’s a three-course meal with dessert. Bon appétit, available here 📗.

In our comprehensive discussion on “Cannabinoid Receptors and Chronic Genetic Diseases,” we have delved into the intricate relationship between cannabinoid systems and the management of genetic conditions. The role of cannabinoid receptors in genetic disorders opens a new avenue for understanding how THC and CBD may influence the progression and symptomatology of these diseases.
The impact of THC and CBD on chronic genetic diseases has become a focal point for researchers aiming to uncover new therapeutic strategies. With cannabinoid therapy for hereditary diseases showing promise, there’s growing interest in how CBD effects on gene expression might contribute to symptom management and potentially slow disease progression.
THC modulation of genetic disease symptoms, alongside broader investigations into cannabinoids and their influence on genetic disorders, suggests that these compounds may interact with genetic mutations in a way that could mitigate some of the adverse effects of these conditions. This possibility is supported by studies looking into the benefits of cannabis in managing chronic genetic illnesses, emphasizing the need for in-depth cannabinoid receptor research in genetic disease treatment.
As we explore how cannabinoids affect genetic disease progression and the specific roles of CB1 and CB2 receptors in hereditary disorders, the therapeutic potential of cannabis in genetic disorders becomes increasingly clear. This includes not only the symptom management benefits of CBD and THC but also the potential for cannabinoids to serve as therapeutic agents for a range of genetic conditions.
Research into the efficacy of cannabinoids in providing symptom relief for genetic diseases has laid the groundwork for further exploration into cannabinoid receptors’ impact on genetic disease mechanisms. As we continue to uncover the therapeutic potential of cannabis in this context, the role of CBD in genetic disease management and THC’s effects on chronic genetic disease treatment highlight the nuanced ways in which these substances interact with the body’s own systems.
Looking forward, the future directions in cannabinoid therapy for genetic diseases are ripe with potential. As research continues to advance, the integration of cannabinoids into treatment regimens for genetic conditions offers hope for improved patient outcomes and a deeper understanding of both cannabinoid science and genetic disease mechanisms. The exploration of cannabinoids in the context of chronic genetic diseases represents a frontier in medical research, promising new insights and therapeutic options for those affected by these complex conditions.
