From Raw Cannabis to Final Product: The Ethanol Extraction Journey
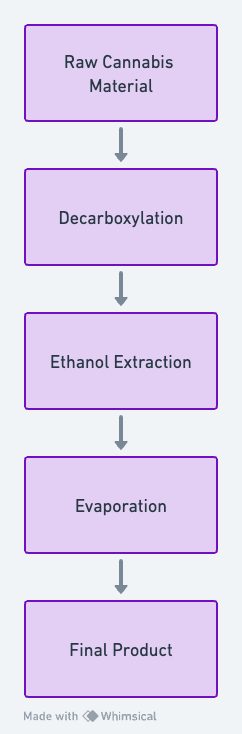
This diagram maps the journey of raw cannabis material through the processes of decarboxylation, ethanol extraction, and evaporation, culminating in the final product. The step-by-step guide enables a nuanced understanding of the entire process.
Decarboxylation: Raw cannabis must first undergo decarboxylation to activate its key components, like THC and CBD, by removing the carboxyl group through heat application.
Ethanol Extraction: Ethanol serves as the chosen solvent for its polarity, which enables the extraction of a broad spectrum of cannabinoids and terpenes. However, it may also pull out undesirable compounds like chlorophyll, requiring further filtration steps.
Evaporation: Post-extraction, ethanol is evaporated to leave behind the concentrated cannabis extract.
Homemade vs. Professional Setups: While homemade versions often employ simple setups such as rice cookers for evaporation, professional setups use more controlled environments like rotary evaporators, enhancing both yield and purity.
Rationale for Ethanol Extraction: Ethanol is chosen for its safety, efficiency, and the broad spectrum of compounds it can extract. It’s also food-safe, which adds an extra layer of security for medicinal and recreational users alike.
Advantages and Disadvantages: Ethanol is efficient and relatively non-toxic but may extract unwanted compounds and may require more sophisticated filtration techniques.
Homemade Recipe Consideration: For those interested in DIY ethanol extraction, the recipe involves decarboxylating the raw cannabis in an oven, soaking it in ethanol, and then evaporating the ethanol using a simple heat source. However, caution should be exercised due to the flammable nature of ethanol.
📗 Note: If the diagram’s the opening credits, the book is the director’s cut. Roll the film by clicking here 📗


